- Your are here:
- NEWS
Milling of polymer and composite materials
 Upload to:05-27 2021
Upload to:05-27 2021
The scope of polymeric materials (plastics) is continuously expanding. At the same time, extrusion and other methods of moulding products do not allow to produce some types of parts. This necessitates improvements in polymer processing technologies. Fraser machines with CNC allow to significantly expand the range of products from plastics and composite materials (reinforced plastics).
COntent:
1.Differences between plastics and metals
2.Types of polymer and composite materials
3.Choosing processing modes
4.Choosing a tool and snap

1. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PLASTICS AND METALS
When it comes to metal processing,for most professionals, the differences between aluminum, carbon and stainless steel are obvious. The difference in mechanical properties requires the choice of different cutting modes, tools, dressings and machines. Despite the fact that the vast majority of plastics and composites are softer than metals, it is also impossible for them to find a universal method of processing. When milling polymer and composite materials, especially soft materials, often have to face the problem of choosing a mode that will allow you to work with high performance and get parts with specified parameters of roughness and dimensions.
In comparison with metals, polymeric materials have a wide range of technological advantages:
Low density
Electrical insulation properties and the ability to regulate conductivity;
Resistance to most active chemicals, including acids, alkaline, organic solvents;
Low vibrativity
heat insulating properties;
Recycling.
At the same time, they have a number of drawbacks that limit their use:
Relatively low heat resistance;
High heat expansion rate
Small hardness;
propensity for creep.
When choosing a regimen for processing a polymer material, it is worth paying attention to its softening and melting temperatures, as well as the thermal conductivity. Excessive heat production in the cutting area leads to the accumulation of internal stresses, as a result of which the blanks are hogged, cracks appear and the part is destroyed. Also, because of the linear extension, size tolerances may not be met. The milling technology should be built in such a way as to dissipate heat as much as possible. And the best way to remove it from the cutting area is the timely removal of shavings.

2. TYPES OF POLYMER AND COMPOSITE MATERIALS
Depending on the maximum operating temperature, plastics are divided into the following types:
standard - polyethylene, polypropylene, ABS;
engineering - PET (polyethylenerephthat), polyoxymethylene, polyamide;
high-temperature - fluoroplasts, some types of polyamides, niplone.
For ABS plastic, it is -70...-70 degrees Celsius.
Thermoplastic polymer materials are divided into two types:
Amorphous. These materials are highly thermostability, i.e. relatively low temperature expansion. When prescribing a treatment regimen, you need to be especially careful: amorphous plastics have a tendency to form internal stresses during molding. Too high a supply can lead to cracks.
Semi-crystal. This type of plastic is not so much prone to the formation of cracks, is characterized by high elasticity and good shock viscosity. At the level of formation in semi-crystal plastics remain zones with crystal lattice, and they are stress hubs. Overheating of the blank during milling can lead to their release and deformation of the product.
The compositional materials have a more complex structure. Their strength and processing are determined by the following factors:
The strength of the matrix;
Filler properties
Clutch material components
composite structure.

3. CHOOSING PROCESSING MODES
When choosing processing modes, it is important to take into account the rigidity of fixing the blank to the machine, the hardness of the blank, the conditions of the shavings, cooling. When milling metals, increasing the cutting speed and reducing the supply reduces resistance to the material being processed and increases the durability of the instrument. For plastics, this strategy is not suitable, because it will lead to increased heat production. Fraser processing of polymeric materials is carried out mainly on high pitches.
There are several general recommendations for milling polymeric materials:
1.Cast blanks are less prone to hogging than extruded blanks. Many manufacturers of polymeric materials offer a sheet, a circle and a pipe with thermal treatment. Such a blank has no internal stresses and allows to achieve good accuracy of sizes.
2.Excess heat is well excreted by removing the shavings. When milling plastics, cooling is done with compressed air or regular water.
3.Milling soft plastics is done with single-loading cutters with polished groove to remove shavings.
4.The spindle turns are chosen so that the shavings were crumbly.
5.In oncoming milling roughness is lower than in passing.
6.Surface quality is improved if the clean treatment is carried out with a intake of 0.2 - 0.5 mm field of complete cooling of the blank.
One of the most serious problems with milling is twisting shavings on the cutter. To solve this problem on BCAMCNC machines, we recommend cutting at a low feed speed,and then increase it to optimal. When milling grooves apply a spiral motion of the instrument. Drilling holes are performed in several passages with full extraction of cutter, drill or engraver.
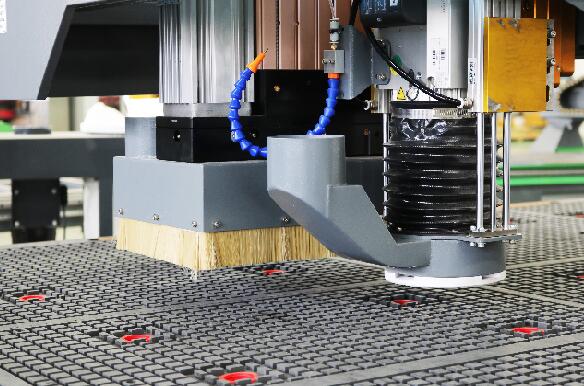
4. CHOOSING A TOOL AND SNAP
For milling polymer and composite materials, you need to choose a tool with a high quality cutting edge treatment. The fres,sharpened on an abrasive stone, will leave traces on the surface of plastics, and the polished cutting edge will give an acceptable quality of treatment. When sharpening the cutters to reduce the roughness of the surface perform a drum tick.
Polymer cutters are made of fast-cutting steel, solid alloys and polycrystalline diamond. The durability of the work edge and the performance of the tool depend on the hardness of the blank and the cutting edge material. To increase the resource of the cutters of fast-cutting steels on them apply wear-resistant coatings, such as titanium nitrid.
When fixing plastic on your desktop, it's important to find the optimal compression force. If it is lower than necessary, the blank will vomit during processing. Too much effort can cause deformation and cracks. Vacuum tables are best suited to secure sheet materials. They provide reliable fixation and do not deform plastic.
All BCAMCNC portal milling machines are equipped with vacuum tables and can be used to process polymer materials.
- Previous : Frequently asked questions before Purchase CNC ROUTER
- Next : Making furniture By CNC wood router


 EN
EN Ru
Ru